Nuclear Extract Kit Overview
The Nuclear Extract Kit isolates high-quality nuclear, cytoplasmic or whole-cell extract from mammalian cell or tissue samples. This eliminates the need for optimizing reagents and protocols, and ensures high yields every time. More importantly, standardizing your extraction procedure with our high-quality reagents ensures more reproducible results. Extracts are suitable for use in a various applications including EMSA, Western blot and binding assays and is ideally suited for preparation of extracts for our TransAM® Transcription Factor Assays.
The Nuclear Extract Kit works with fresh or frozen cell and tissue samples and yields protein amounts of approximately 0.5 to 1 mg from cytoplasmic extract (at 1-2 mg/ml concentration), 150 to 250 μg from nuclear extract (at 3-5 mg/ml concentration), 1.2 to 2.4 mg from whole cell extract (at 4-8 mg/ml concentration) from 8.8 x 106 cells. The kit procedure is simple and only takes two hours to complete. The kit includes buffers, detergents and reagents for lysis as well as Protease and Phosphatase inhibitors to ensure preservation of your proteins.
Applications
Extracts prepared using the Nuclear Extract Kit can be used with Active Motif’s TransAM® Kits, or in other procedures that require cell extracts, like gelshift assays, Western blots, DNA footprinting, as a starting point for protein purification for binding or activity assays or or other analysis techniques.
Nuclear Extract Kit Advantages:
- Quality-controlled reagents ensure reproducibility
- No need to optimize your own procedure
- Complete kit contains all required reagents
- Prepare nuclear, cytoplasmic or whole-cell extracts with one kit
Nuclear Extract Kit Contents
Contents & Storage
The Nuclear Extraction Kit is shipped on dry ice and contains reagents with multiple storage temperatures inside. Please store each component at the temperature indicated below. All reagents are guaranteed stable for 6 months from date of receipt when stored properly.
- 1 M DTT (Dithiothreitol); Store at -20°C
- Protease Inhibitor Cocktail (PIC); Store at -20°C
- Lysis Buffer AM1; Store at 4°C
- 10X PBS; Store at 4°C
- Phosphatase Inhibitors; Store at 4°C
- 10X Hypotonic Buffer; Store at 4°C
- Detergent; Store at 4°C
Nuclear Extract Kit Data
To demonstrate the efficiency of cellular fractionation using the Nuclear Extract Kit, nuclear, cytoplasmic, and whole-cell extracts were prepared from HeLa cell samples. Nuclear pellets from the nuclear extraction were also collected. Cellular fractions were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against various proteins. As shown in Figure 1, proteins that serve as markers for cellular fractionation, such as nuclear marker RNA pol II and cytoplasmic marker alpha Tubulin, were only detected in their respective cellular fractions and in whole-cell extracts. The localization of other proteins, such as membrane-associated Lamin A/C and pan-Cadherin, mitochondrial COX IV and GAPDH were also analyzed.
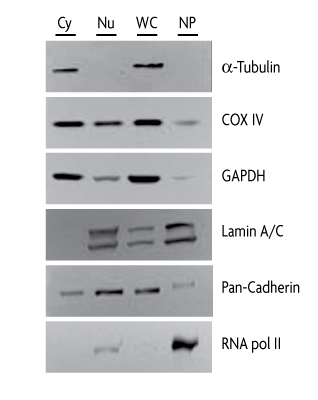
Figure 1: Western blots of specific proteins from cellular fractions obtained with the Nuclear Extract Kit.To evaluate the efficiency of cellular fractionation, 20 μg of nuclear (Nu), cytoplasmic (Cy) and whole-cell (WC) extracts, along with nuclear pellet collected during nuclear extraction using the Nuclear Extract Kit were analyzed by Western blot using antibodies against various specific proteins. Primary antibodies: Active Motif alpha Tubulin, Catalog No. 39528; COXIV; GAPDH; Active Motif Lamin A/C, Catalog No. 39288; Pan-Cadherin; Active Motif RNA pol II, Catalog No. 39097.
To demonstrate the quality of the materials and protocol of the Nuclear Extract Kit, nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts were prepared from HeLa cell samples that were either unstimulated or stimulated with TNF-α for 30 minutes. Because activated NFκB translocates into the nucleus, only nuclear extract from stimulated cells should contain activated NFκB. As predicted, this is precisely what was seen (Figure 2), demonstrating the kit’s high specificity.
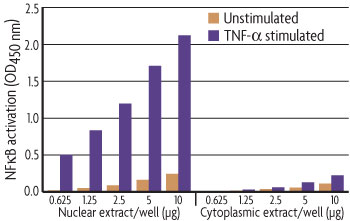
Figure 2: Specific extraction of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts.NFκB activation was assayed with the TransAM® NFκB p50 Kit using increasing amounts of nuclear and cytoplasmic extracts isolated from unstimulated and stimulated HeLa cells using the Nuclear Extract Kit.
Active Motif also offers a number of ready-to-use nuclear, cytoplasmic and whole-cell extracts. These extracts have been prepared using the same high-quality components found in the Nuclear Extract, and many are supplied as positive controls in TransAM Transcription Factor DNA-binding ELISAs.
Nuclear Extract Kit Publications
Search our database of customer publications that have used our Nuclear Extract Kit.
Nuclear Extract Kit Documents