ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Services Overview
A common problem with traditional ChIP-Seq protocols is that they are not always able to detect global changes in histone modifications caused by treatment with small molecule epigenetic inhibitors.
Active Motif's ChIP-Seq experts have developed and validated a solution to solve this problem, and this novel spike-in and normalization strategy is now included in our end-to-end ChIP-Seq services.
How does ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization work?
A relatively minor change to the standard ChIP-Seq protocol allows the assay to become more quantitative and enables identification of global changes in levels of histone modifications or transcription factor binding profiles across the genome.
The ChIP-Seq spike-in normalization method starts by setting up a standard ChIP reaction using experimental chromatin (e.g. human) and an antibody of interest. In addition, Drosophila melanogaster chromatin is "spiked-in" to each reaction as a minor fraction of the total chromatin. An antibody that recognizes the Drosophila-specific histone variant, H2Av, is added to the reaction. The Spike-in Antibody provides a mechanism to reliably pull down a small fraction of the Drosophila chromatin that is consistent across all samples. Following ChIP sequencing, the data is mapped to both the Drosophila genome and the experimental genome. A normalization factor is created for each sample based on the Drosophila tag counts. The experimental tag counts are normalized by the same factor.
For more details, read our PLoS One publication about this spike-in normalization technique:
Egan B, Yuan C-C, Craske ML, Labhart P, Guler GD, Arnott D, et al. (2016) An Alternative Approach to ChIP-Seq Normalization Enables Detection of Genome-Wide Changes in Histone H3 Lysine 27 Trimethylation upon EZH2 Inhibition. PLoS One 11(11): e0166438. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0166438
For additional information, please check out our on-demand webinar on ChIP-Seq spike-in normalization.

ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Service Data
Biases that are introduced during next-generation sequencing library amplification and sequencing also occur with the Drosophila spike-in chromatin. However, normalization using our Spike-in strategy eliminates these biases, enabling ChIP-Seq analysis to reveal any significant biological changes present in your samples.
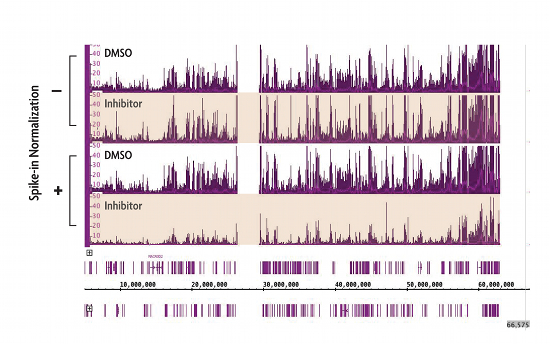
Figure 1: ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Strategy reveals changes in H3K27me3 levels following treatment with EZH2 inhibitor compound.
Cells treated with small molecule inhibitors of the EZH2 methyltransferase have dramatic reductions in global H3K27me3 levels. However, H3K27me3 ChIP-Seq using standard ChIP-Seq protocols do not detect these differences (indicated by the - label). Incorporation of Active Motif’s ChIP-Seq Spike-in strategy reveals the expected decrease in H3K27me3 ChIP-Seq signal (indicated by the + label).
ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Service Publications
Search our database of customer publications that have used our ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization services.
ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Service Documents
ChIP-Seq Spike-in Normalization Service Sample Submission Portal
Our online sample submission portal allows you to easily upload your service project samples and track your project status. Follow the sample submission instructions in the portal to ensure that all your samples arrive at Active Motif in the best possible condition and properly associated with your project.