Mod Spec® Service Overview
Mod Spec® is a mass spectrometry method that is used to measure the relative abundance of > 60 different histone modifications. Mod Spec® is a great starting point to determine if epigenetic changes are occurring in response to disease or treatment. The large number of modifications monitored allows researchers to not only observe expected changes, but to discover unexpected changes, which can be even more informative.
Analyze histone modification changes in:
- Response to epigenetic inhibitors
- Normal vs diseased cells
- Knock-out cells or animals
- Inhibitor treated xenografts
- Human biopsies
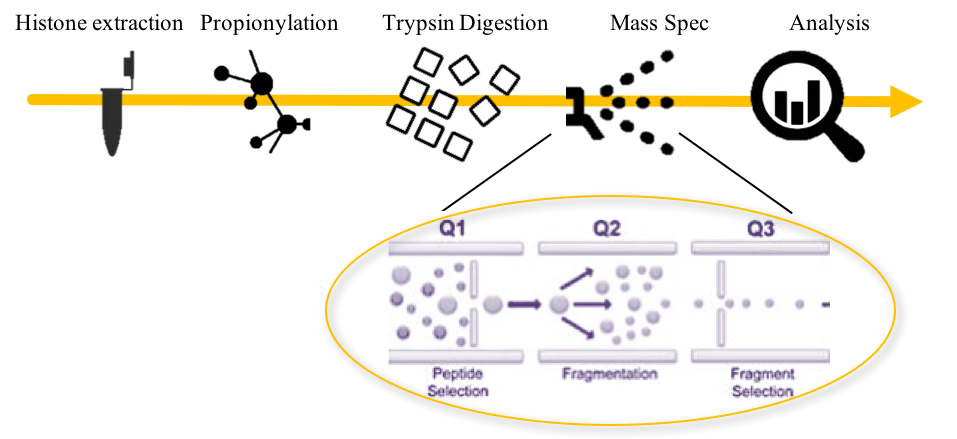
How Does Mod Spec® Work?
1. Histone Extraction: From 2-5 million cells or 25-100 mg tissue.
2. Propionylation: Mass spectrometry of proteins requires digestion of the proteins into small peptides before injection into the mass spectrometer. Propionylation, using propionic anhydride, blocks cleavage at lysines by trypsin, while allowing digestion at arginines to occur. The resulting peptides are of the appropriate size for mass spec analysis.
3. Trypsin Digestion: Histones are digested with trypsin.
4. Mass Spec: Samples are analyzed on a Triple-Stage Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer.
- Q1: Peptides of the appropriate molecular weight are selected.
- Q2: Peptides are further fragmented in the collision chamber.
- Q3: Peptides fragments of interest are selected and analyzed by mass spectrometry.
5. Analysis: Fragments are analyzed and graphed to show changes between samples.
Histone Modifications Detected by Mod Spec®
^ Multiple H2A isoforms may contribute to the signal for modifications on H2A.
* H3R2me2 and H3K4me2/3 are mutually exclusive modifications. H3R2 methylation prevents H3K4 methylation. Therefore, H3K4 modifications are reported only on the H3R2 unmodified peptide. For more information, see Nature. 2007 Oct 18; 449(7164):933-7.
♦ H3.2 may contribute to signals for modifications labeled H3.1.
What our customers are saying about us:
"While working on the molecular mechanism of an epigenetic drug, we outsourced Mod Spec® to Active Motif in order to get a broader overview of the drug-induced changes of histone modifications. Overall, we were very pleased with the quality of the service, the kept timeline and last but not least, the fair price. We found surprising things that were not on our radar before."
Matthias Lauth, PhD
Phillips University
Marburg, Germany
View complete list of testimonials >
Mod Spec® Service Data
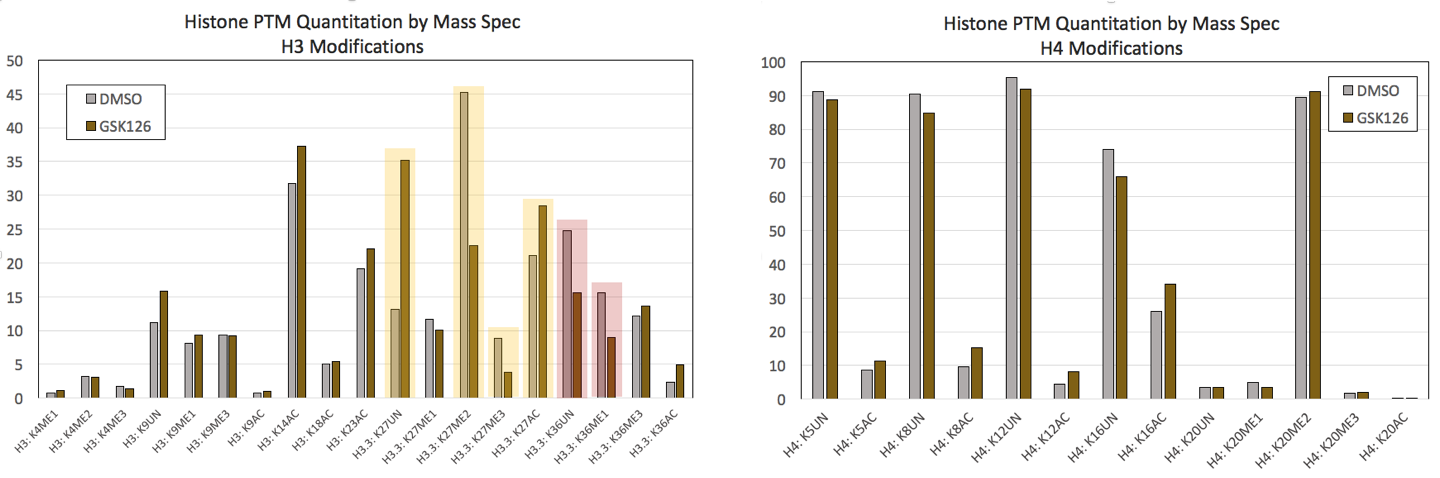
Figure 1: Mod Spec® data from control HeLa cells and HeLa cells treated for 7 days with 0.5uM GSK-126.(Click image to enlarge)
GSK126 is an inhibitor that blocks the methytransferase activity of EZH2, resulting in global decreases in H3K27me2 and H3K27me3. A) A selection of H3 modifications are shown from Active Motif’s Mod Spec® assay that confirm significant decreases in H3K27 methylation with concomitant increases in acetylated and unmodified H3K27 (highlighted in yellow). Changes at H3K36 were also detected (highlighted in red). B) A selection of H4 modifications do not show significant changes in response to GSK126 treatment.
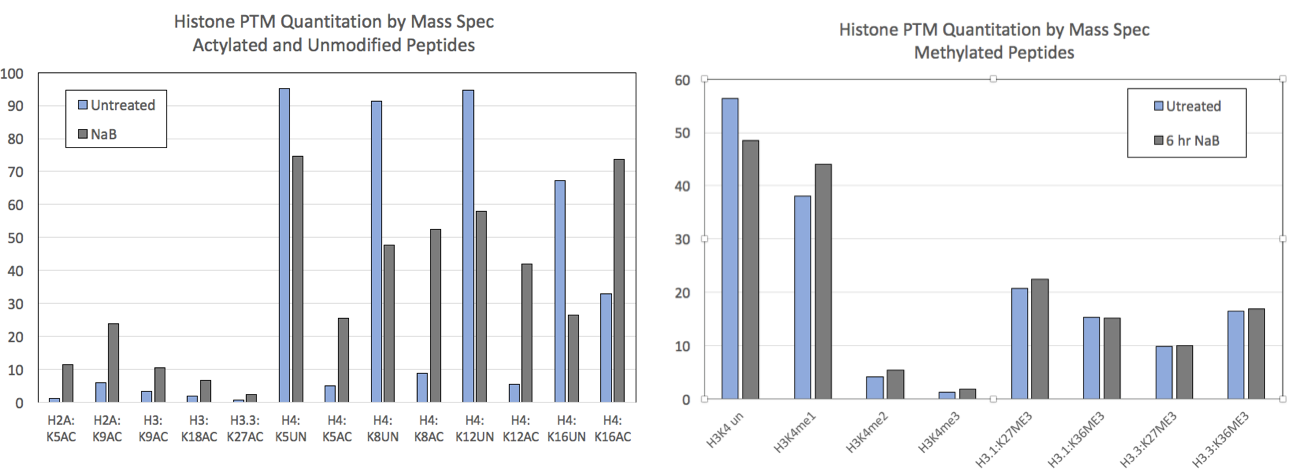
Figure 2: Mod Spec® data from control HEK293 cells and HEK293 cells treated for 6 hours with 5 mM sodium butyrate (NaB).
NaB is a general HDAC inhibitor and treatment is expected to increase histone acetylation levels. A) Mod Spec® data for a selection of acetylated and unmodified histone sites is shown. Acetylation is increased at all sites after treatment. Unmodified peptide is displayed for some sites and shows a concomitant decrease after NaB treatment. B) Methylation at various histone residues is not affected by NaB treatment.
Mod Spec® Service Publications
Search our database of customer publications that have used our Mod Spec® services.
Mod Spec® Service Documents
Mod Spec® Service Sample Submission Portal
Our online sample submission portal allows you to easily upload your service project samples and track your project status. Follow the sample submission instructions in the portal to ensure that all your samples arrive at Active Motif in the best possible condition and properly associated with your project.
You might also be interested in:
| Name | Cat No. | Price | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mod Spec® | 25085 | Get Quote | |